Child Development: A Complete Guide to the Essential Stages
Urinary Tract Infections in Children: Symptoms and Treatment
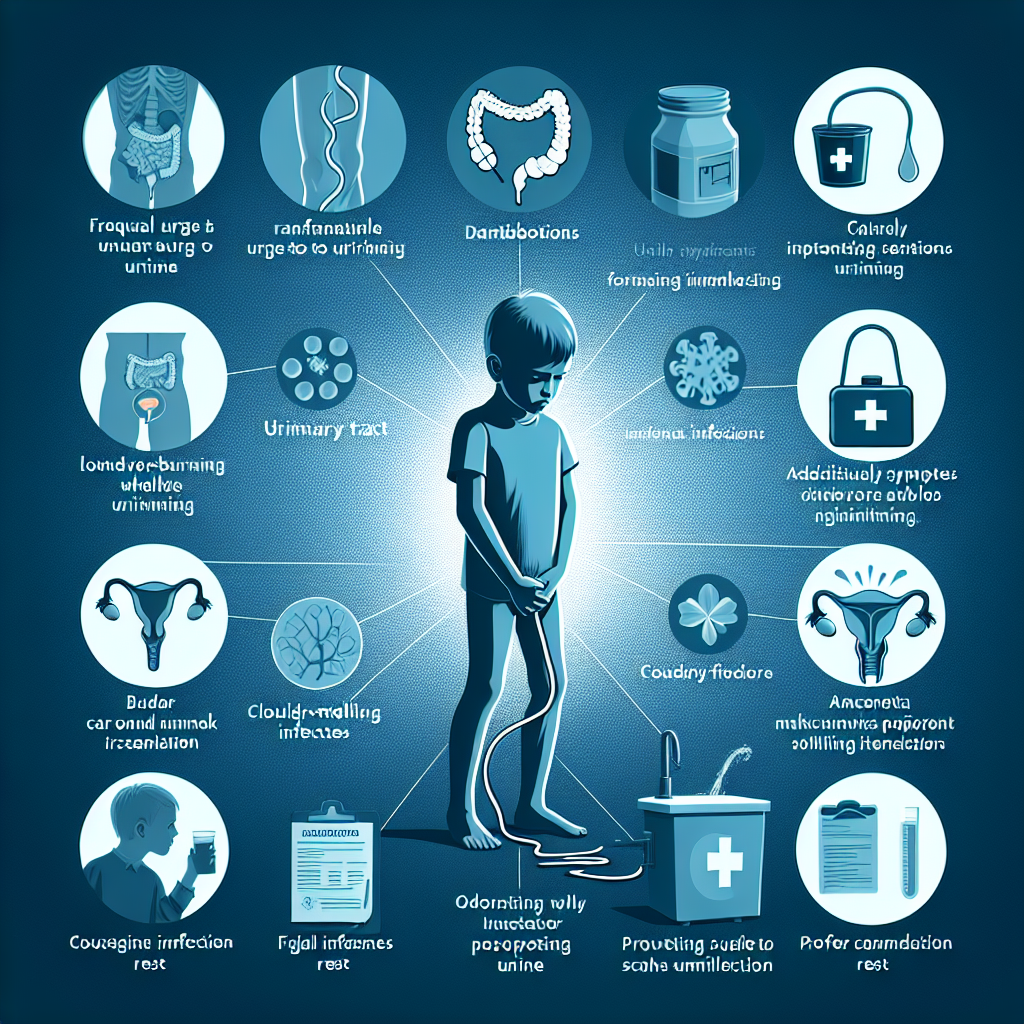
Urinary tract infections are a common health problem seen in children and can be a source of concern for many parents. Understanding the symptoms and how these infections can be treated is crucial to ensuring the well-being of our little ones.
Identifying Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection in Children
UTI symptoms in children can vary depending on age and the severity of the infection. In general, common signs include:
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating
- Frequent and/or urgent urination
- Abdominal or lower back pain
- Fever, chills or night sweats
- Strong or unusual smelling urine
- The presence of blood or turbidity in the urine
It is important to note that in infants and very young children, symptoms may be less obvious, such as unusual irritability, lack of appetite or vomiting.
Causes and Risk Factors
UTIs are often caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, usually through the urethra. Certain conditions can increase your risk of developing this condition, such as:
- Abnormalities of the urinary tract
- Chronic constipation
- Inadequate hygienic practices
- Frequent use of antibiotics
- Vesicoureteral reflux (when urine backs up from the bladder into the ureters)
Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections
Diagnosis is based on evaluation of symptoms, physical examination and, most importantly, laboratory tests. Common tests include:
- Uroculture, which identifies the type of bacteria and sensitivity to antibiotics
- Urine summary, which detects the presence of red cells, white cells and bacteria
- Renal and bladder ultrasound, in case of frequent recurrences, to identify possible structural abnormalities
Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
Treatment of urinary tract infections in children usually includes the administration of antibiotics, the duration and type of which will be determined by the doctor depending on the severity of the infection and the result of the urine culture. It is crucial that the treatment is followed exactly to prevent complications and recurrence of the infection.
Methods of Prevention
The prevention of urinary infections in children involves some simple but effective measures:
- Encourage adequate fluid intake, especially water
- Promoting proper hygiene, such as washing properly after using the toilet
- Avoiding constipation through a balanced, high-fiber diet
- Quick change of soiled diapers in infants
- Using cotton underwear and avoiding clothing that is too tight
Unfinished Follow-ups and Potential Complications
If left untreated, UTIs can lead to serious complications, including:
- Pyelonephritis - a kidney infection that may require hospitalization
- Sepsis - a generalized infection of the whole body
- Renal scarring - can affect kidney function in the long term
Constant Medical Supervision
It is essential that parents work closely with health care professionals for proper monitoring and treatment of UTIs in children. This includes regularly tracking your symptoms, following your treatment plan, and scheduling follow-ups.
When to Seek Medical Help
Any suspicion of a urinary tract infection in a child should prompt a visit to the doctor. Signs that require immediate attention include:
- High fever
- Persistent vomiting
- Severe back or abdominal pain
- Marked changes in behavior or feeling unwell
Conclusion
In conclusion, urinary tract infections in children are frequently treated conditions but require proper attention and care. Recognizing early symptoms and ensuring prompt treatment can prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery. By adopting preventive measures and carefully monitoring the child's health, parents can play an essential role in maintaining their well-being. If you have any questions or concerns about your child's health, do not hesitate to consult a specialist.